As a result of the meeting ended on Wednesday, the Fed kept the current parameters of its monetary policy unchanged. Recall that since March 2020, the US central bank has kept interest rates in the range of 0% - 0.25%, and since July 2020, it has been buying back assets in the bond market in the amount of $ 120 billion every month.
For several months in a row, Fed officials have continued to declare that they will continue their stimulus policy until the economy demonstrates "further significant progress" in achieving the central bank's goals of low unemployment and 2.0% annual inflation. On Wednesday, the central bank noted that there is progress in this direction, and also announced its intention to continue to assess the degree of progress in future meetings.
"Against the background of progress in vaccination of the population and strong government support measures, indicators of economic activity and employment continue to grow stronger. The sectors most affected by the pandemic have shown some improvement, but have not yet fully recovered", the central bank said.
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell, during a press conference after the meeting, again promised financial market participants to send a signal before the Fed begins to reduce the volume of purchases. Earlier, he said that the conditions for such a step on the part of the FRS have not yet emerged, and the economy is very far from the required indicators.
The US dollar weakened on Wednesday after the Fed meeting, and the yield on 10-year US government bonds fell to 1.226%, although, in early April, it exceeded 1.700%, rising on expectations of an economic boom due to vaccination of the population against coronavirus and fiscal stimulus measures.
The decline in the yield on government bonds indicates an increase in demand and prices for them, which is partly due to continued purchases from the Fed and the preservation of some caution among investors amid the ongoing spread of the coronavirus, less confidence in the long-term prospects for economic growth and less concern about inflation.
One way or another, the fall in the yield of American bonds puts additional negative pressure on the dollar.
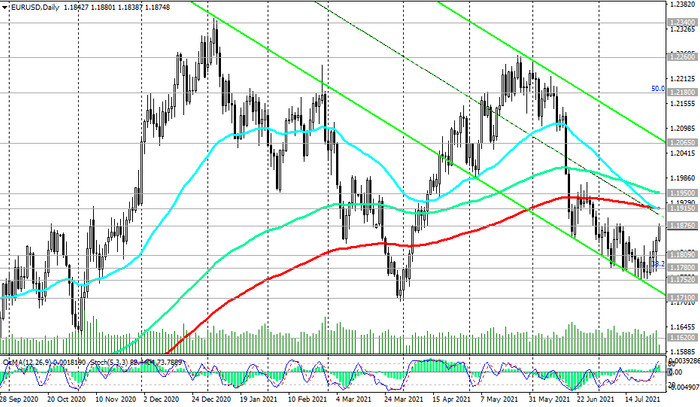
As a result of the July meeting, the Fed softened the tone of its statements and avoided a clear indication of the timing of the start of the withdrawal of stimulus. In general, the results of the last Fed meeting can be described as negative for the dollar, and today the DXY dollar index is declining again, and for the 4th day in a row. As of this writing, DXY futures are traded near 92.05, down 1.2% from last week's high of 93.19.
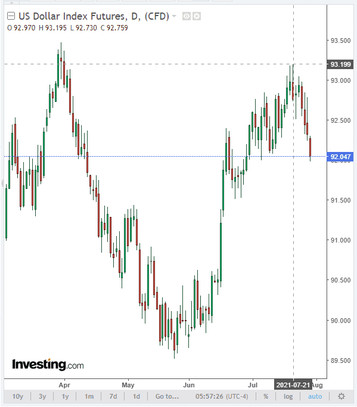
The dollar is likely to remain under pressure for some time, at least until fresh strong macro data starts coming in from the US. So, today investors will pay attention to the publication at 12:30 (GMT) of the preliminary release on US GDP for the 2nd quarter. GDP data is one of the key (along with data on the labor market and inflation) for the Fed in terms of its monetary policy. Strong result strengthens the US dollar; weak GDP report negatively affects the US dollar. In the previous 1st quarter, GDP grew by +6.4%. Another 8.6% growth is expected in the 2nd quarter, which is a positive factor for the dollar. The positive data on GDP will support the dollar and the American stock indices, although they are already mostly included in prices.
If the data turn out to be significantly weaker than forecast or indicate a decline in GDP in the 2nd quarter, then the dollar may react with a strong short-term decline.
Market participants will also pay attention to the weekly data from the US labor market. The US Department of Labor report on the number of jobless claims will also be published at 12:30 (GMT), which will cause additional volatility in the dollar quotes and in the financial markets during this time period. Fed leaders are closely following the progress of the recovery of the labor market in the United States, since they consider the full recovery of the labor market and its return to the levels before the pandemic more important than the rise in inflation. The number of initial jobless claims in the US is expected to fall to 380,000 last week (from 419,000, 368,000, 386,000, 415,000, 418,000 in previous weekly reporting periods), which is a positive factor for the dollar. If the data turns out to be better than the forecast, then the dollar will receive additional short-term support.
And tomorrow, market participants will study the Eurostat report on the Eurozone GDP. Recently, macro data has been coming from the Eurozone, indicating a gradual recovery in the growth rate of the European economy after a sharp drop in early 2020.
According to economists' forecast, GDP growth in the Eurozone is expected in the 2nd quarter of 2021 by +1.5% (+13.2% in annual terms), which is a positive factor for the euro. These data and indicators, better than the forecast, may strengthen the euro in the short term, although it is still far from the full recovery of the European economy even to pre-crisis levels.
If the data turn out to be weaker than the forecast, then the euro may decline, including against the dollar.
One way or another, the US economy is recovering faster than the Eurozone economy, and the growing US inflation, which shows the highest growth rates in almost 30 years, will sooner or later force the Fed leaders to pay attention to this and still begin to curtail the stimulating policy. Most economists believe that the Fed will start this process earlier than the ECB. And this is one of the main reasons to give preference to still short positions on the EUR / USD pair, especially during periods of its correctional growth, for example, such as at the moment.