Introduction
The stock market performance has in the past been linked to the performance of a country’s economy. This relationship isn’t always true. However, there is a direct correlation between the performance of a country’s capital market and the performance of the domestic currency in the forex market.
The primary relationship between the stock market and the forex market has to do with capital inflow when the stock market is performing well, and capital flight when the stock market is performing poorly.
Furthermore, the forex trading sessions in most countries coincide with the opening and closing of the stock markets. During these sessions, the increased trading activities means that foreign investors have to either convert foreign currencies into domestic currencies to buy into the domestic stock markets when it is performing well. Similarly, foreign investors may have to sell the domestic currency and buy foreign currencies when exiting the domestic stock market.
In this article, we will explore these relationships and explain their implications for a retail forex trader.
How the Stock Market Performance is Measured?
The best measure of the performance of any stock market is by using indices. The stock market indices aggregate a significant portion of the companies listed in an exchange and serve as a benchmark for the whole stock market.
For this analysis, we’ll use the US30 and US500 and for the US stock markets, and FTSE 100 for the UK. We will compare the performance of these indices when the stock market was on an uptrend and downtrend, with the performance of the domestic currency in the forex market.
When the Stock Market is on an Uptrend
The first thing we have to understand is that the value of a country’s currency is almost entirely dependent on the forces of demand and supply. When the currency is in high demand – meaning it has net buyers in the market – its value will increase. Conversely, when the demand for a currency is lower – meaning it has net sellers – its value decreases.
Now, when a country’s stock market is performing well, it is natural for foreign investors to be attracted to the domestic market. It is common knowledge that capital will flow where investments are performing well.
When foreign investors want to invest in the domestic stock markets, they will have to convert their currencies into the local currencies in the domestic currency in the forex market. As a result, there will be an increased demand for the domestic currency in the forex market. Based on the laws of demand and supply, this increase in demand will lead to an increase in the value of the domestic currency relative to other currencies.
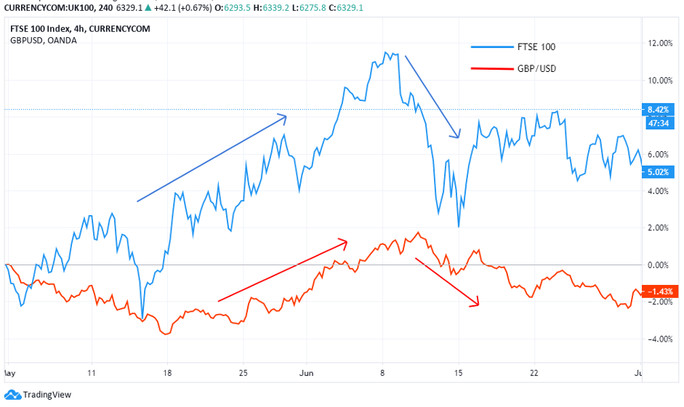
Let’s take an example of the US stock market as measured by the FTSE 100 and the performance of the GBP.
Notice that a bullish FTSE 100 corresponds to a bullish GBP/USD. A bullish FTSE 100 could correspond to a net inflow of foreign investors into the UK capital market. Consequently, the demand for the GBP results in its appreciation against other currencies in the forex market.
When the Stock Market is on a Downtrend
When the stock market is on a downtrend, it implies that investors are nor receiving higher returns or worse, risk losing their capital. The sell-off will result in a drop in the stock market indices. In this case, foreign investors might pull out their capital from the stock markets and seek higher returns in other better-performing markets.
While exiting, foreign investors may convert their money into other currencies. This involves selling the domestic currency in the forex market and purchase other foreign currencies. It results in the excess supply of the domestic currency relative to its demand. Based on the laws of supply and demand, the increase in supply will make the domestic currency depreciate relative to other currencies in the forex market.
However, a poorly performing stock market isn’t the only reason foreign investors pull out. Foreign investors can also pull out as a result due to profit-taking. If investors believe that there is no more room for growth in the near term, they might pull out their capital to invest in more lucrative ventures. In this case, they will also convert the domestic currency into foreign currency leading to the depreciation of the domestic currency in the forex market.
Note that capital flight from the stock market isn’t always a result of poor performance. It can also be a result of profit-taking by foreign investors.
The Comparison
The relationship between a country’s capital market performance doesn’t always correspond match with the performance of the domestic currency in the forex market. Let’s look at the performance of US30 and US500 compared to that of the USD in the forex market during the coronavirus pandemic.
Notice that the rise of the US30 corresponds to the weakening of the USD since the EUR/USD pair is bullish.
Remember that fundamentally, the value of a county’s currency is driven by the country’s economic fundamentals. In the US, for example, as the pandemic ravaged the economy, almost every fundamental economic indicator pointed towards deteriorating economic conditions hence the persistent weakening of the USD.
More so, at the onset of the pandemic towards the end of the first quarter of 2020, the resultant stock market sell-off sent the US30 and US500 indices tumbling. However, investors were quick to return to the stock market to take advantage of the historic low prices. Furthermore, both indices were boosted by the surge in technology stocks like Apple and Microsoft. In this scenario, the stock market performance went up as the value of the USD dropped in the forex market relative to other currencies.
Effectively, it means that while more investors were returning to the stock market, the higher demand for the USD did not result in its appreciation in the forex market. With the knowledge from this article, you can engage in SDS trading .
Conclusion
We can, therefore, conclude that under normal market conditions, the performance of a country’s stock market is directly correlated to the domestic currency’s performance in the forex market.